The Horizontal Integration Differs From Vertical Integration In That It article we provide is expected to provide useful information for you, all of which we have summarized well.
Horizontal vs Vertical Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of business strategy, two key concepts that shape corporate structures and operations are horizontal and vertical integration. Understanding the differences and applications of these integration strategies is crucial for companies seeking to optimize their value chains and achieve sustainable growth.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of horizontal and vertical integration, exploring their definitions, historical context, and their impact on business organizations. We will also provide insights into the latest trends and developments in these integration strategies, offering tips and expert advice to help businesses navigate the complex landscape of modern commerce.
Horizontal Integration: A Strategy for Market Expansion
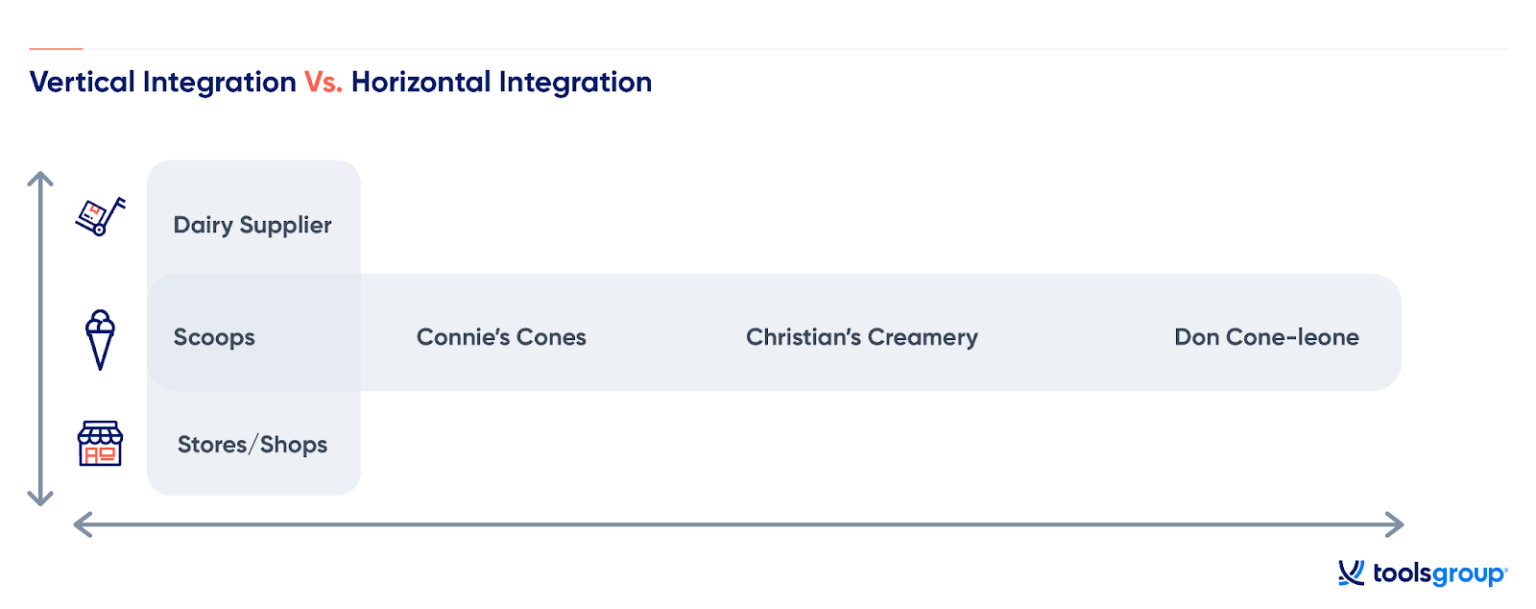
Horizontal integration refers to a business strategy where a company expands its operations by acquiring or merging with other companies operating at the same level of the value chain. In other words, horizontal integration involves consolidating businesses within the same industry and product line.
The primary goal of horizontal integration is to increase market share and reduce competition by combining the resources, capabilities, and customer bases of multiple entities. By eliminating overlaps and inefficiencies, companies can achieve economies of scale, lower production costs, and enhance market power.
Vertical Integration: A Strategy for Value Chain Control
In contrast to horizontal integration, vertical integration involves expanding a company’s operations into different stages of the production process or supply chain. This can include acquiring or merging with suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, or retailers.
The objective of vertical integration is to control more aspects of the value chain, from raw material sourcing to distribution and sales. By doing so, companies can reduce dependence on external suppliers, minimize transaction costs, and ensure the quality and consistency of their products or services throughout the entire process.
The Evolution and Significance of Integration Strategies
The concepts of horizontal and vertical integration have evolved over time, influenced by economic, technological, and regulatory factors. In the early days of industrialization, vertical integration was the dominant strategy as companies sought to secure access to critical resources and control the entire production process.
However, with the rise of globalization and technological advancements, horizontal integration has gained prominence. This is due to the increased importance of economies of scale, reduced barriers to entry, and the need for companies to respond to changing market dynamics.
Benefits and Challenges of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration can offer numerous benefits to businesses, including increased market share, economies of scale, reduced competition, enhanced bargaining power, and potential for synergy and innovation.
However, it also comes with certain challenges, such as regulatory scrutiny, antitrust concerns, the need for careful integration planning, and potential resistance from existing customers or employees.
Benefits and Challenges of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration offers advantages such as greater control over the production process, reduced dependence on external suppliers, increased efficiency, enhanced product quality, and potential for innovation.
On the flip side, it can present challenges related to higher initial investment costs, less flexibility to adjust to changing market conditions, potential conflicts of interest, and the risk of becoming overextended in certain stages of the value chain.
Integrating Technology for Effective Integration
In today’s digital age, technology plays a crucial role in enabling and enhancing both horizontal and vertical integration strategies. Cloud computing, data analytics, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can help companies streamline processes, improve communication, and make data-driven decisions for effective integration.
By embracing technology, businesses can overcome traditional barriers to integration, such as geographical distance or industry-specific complexities, and create more efficient and responsive value chains.
Tips for Successful Integration
To ensure a successful integration process, whether horizontal or vertical, consider the following tips:
- Conduct thorough due diligence: Evaluate potential targets or partners carefully, assessing their financial health, market position, and cultural fit.
- Develop a clear integration plan: Outline the goals, timelines, and execution strategies for the integration process, ensuring alignment with overall business objectives.
- Communicate effectively: Inform and engage stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers, throughout the integration process to minimize uncertainty and build support.
- Manage change effectively: Recognize that integration can disrupt existing operations, so proactively address potential resistance and implement change management strategies to support employees.
- Monitor and evaluate performance: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and make adjustments to the integration plan as needed to ensure it is delivering the desired results.
Expert Advice for Navigation the Integration Landscape
In addition to the tips above, here is some expert advice for navigating the complex landscape of integration strategies:
Consider market conditions: Assess the competitive landscape and industry trends to determine the most appropriate integration strategy for your business.
Leverage external expertise: Seek the advice of experienced consultants or legal experts to guide you through the integration process and minimize potential risks.
Be adaptable and agile: Integration is an ongoing process, so be prepared to adjust your strategy and tactics as market conditions or business needs evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q: What is the difference between horizontal and vertical integration?
A: Horizontal integration involves expanding operations within the same industry, while vertical integration entails expanding into different stages of the production process or supply chain.
-
Q: What are the benefits of horizontal integration?
A: Benefits include increased market share, economies of scale, reduced competition, and enhanced bargaining power.
-
Q: What are the challenges of vertical integration?
A: Challenges include higher initial investment costs, reduced flexibility, potential conflicts of interest, and the risk of overextension.
-
Q: How can technology facilitate integration?
A: Cloud computing, data analytics, and ERP systems can streamline processes, improve communication, and enable data-driven decision-making for effective integration.
-
Q: What are the keys to successful integration?
A: Thorough due diligence, a clear integration plan, effective communication, change management, and performance monitoring are essential for integrating success.
Conclusion
Horizontal and vertical integration are powerful strategies that can help businesses optimize their value
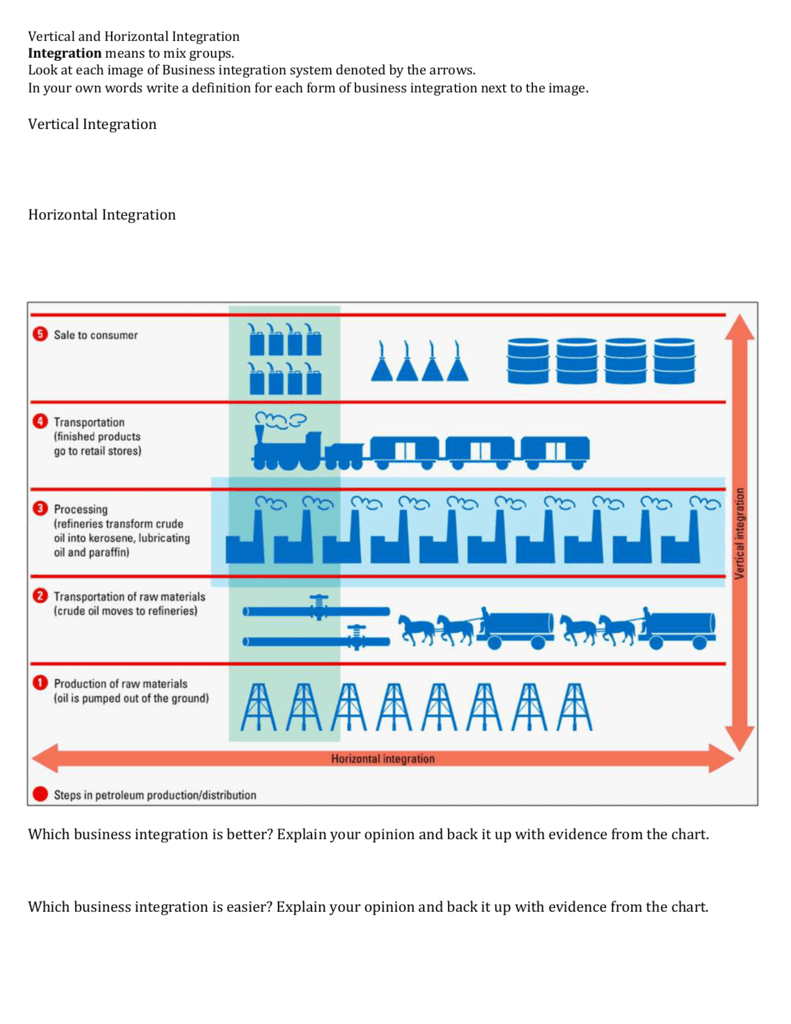
Image: studylib.net
Thank you for visiting our website and taking the time to read Horizontal Integration Differs From Vertical Integration In That It. We hope you find benefits from this article.